WholeMemory Implementation Details#
As described in WholeMemory Introduction, there are two WholeMemory location and three WholeMemory types. So there will be total six WholeMemory.
| Type | CONTINUOUS | CONTINUOUS | CHUNKED | CHUNKED | DISTRIBUTED | DISTRIBUTED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | DEVICE | HOST | DEVICE | HOST | DEVICE | HOST |
| Allocated by | EACH | FIRST | EACH | FIRST | EACH | EACH |
| Allocate API | Driver | Host | Runtime | Host | Runtime | Runtime |
| IPC Mapping | Unix fd | mmap | cudaIpc | mmap | No IPC map | No IPC map |
For “Continuous” and “Chunked” types of WholeMemory, all memory is mapped to each GPU, so these two types are all “Mapped” WholeMemory, in contrast to “Distributed” WholeMemory where all are not mapped.
WholeMemory Layout#
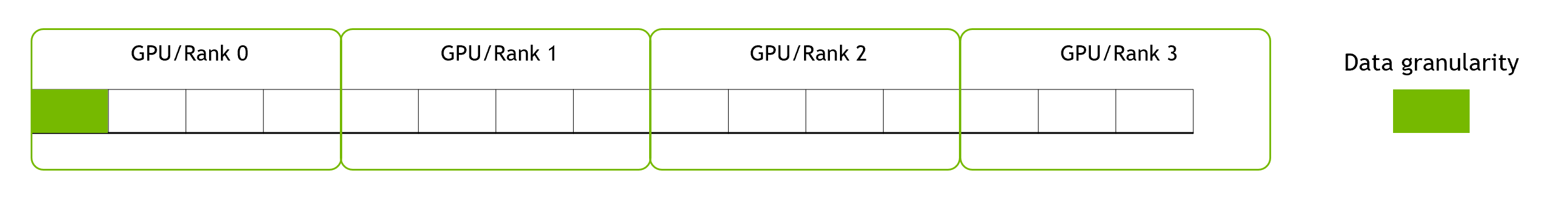
Since the underlying memory of a single WholeMemory object may be on multiple GPU devices, the WholeGraph library will partition data into these GPU devices. The partition method guarantees that each GPU can access one continuous part of the entire memory. Here “can access” means can directly access from CUDA kernels, but the memory doesn’t have to be physically on that GPU. For example,it can be on host memory or other GPU’s device memory that can be access using P2P. In that case the stored data has its own granularity that shouldn’t be split. Data granularity can be specified while creating WholeMemory. Then each data granularity can be considered as a block of data.
The follow figure shows the layout of 15 data block over 4 GPUs.
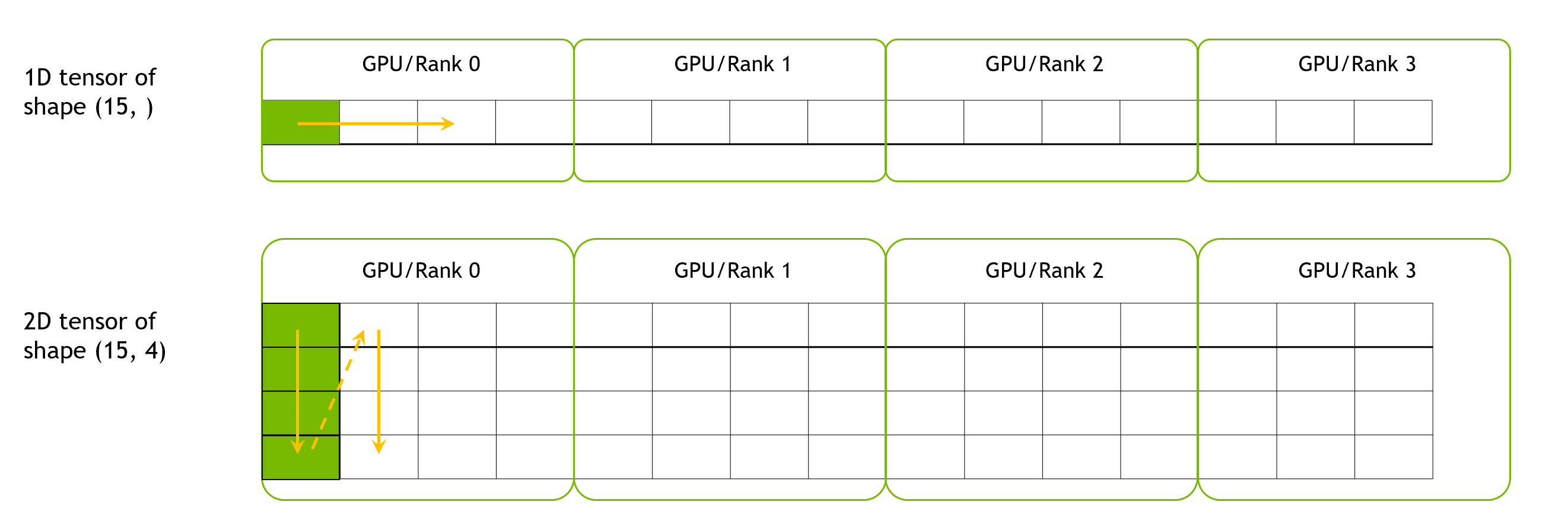
For WholeMemory Tensors, they can be 1D or 2D tensors.
For 1D tensor, data granularity is one element. For 2D tensor, data granularity is its 1D tensor.
The layout will be like this:
WholeMemory Allocation#
As there are six types of WholeMemory, the allocation process of each type are as follows:
Device Continuous WholeMemory#
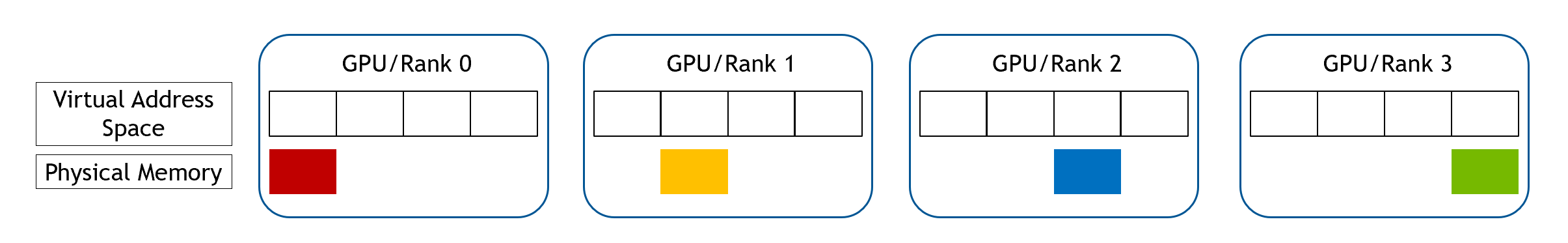
For Device Continuous WholeMemory, first a range of virtual address space is reserved in each GPU, which covers the
entire memory range. Then a part of pyhsical memory is allocated in each GPU, as shown in the following figure.
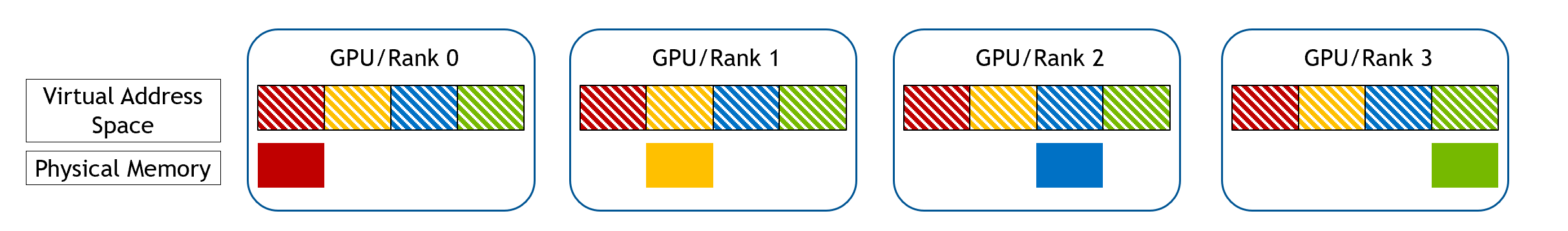
 After that, each GPU gathers all the memory handles from all GPUs, and maps them to the reserved address space.
After that, each GPU gathers all the memory handles from all GPUs, and maps them to the reserved address space.
Device Chunked WholeMemory#
For Device Chunked WholeMemory, first each GPU allocates its own part of memory using CUDA runtime API, this will create
both a virtual address space and physical memory for its own memory.
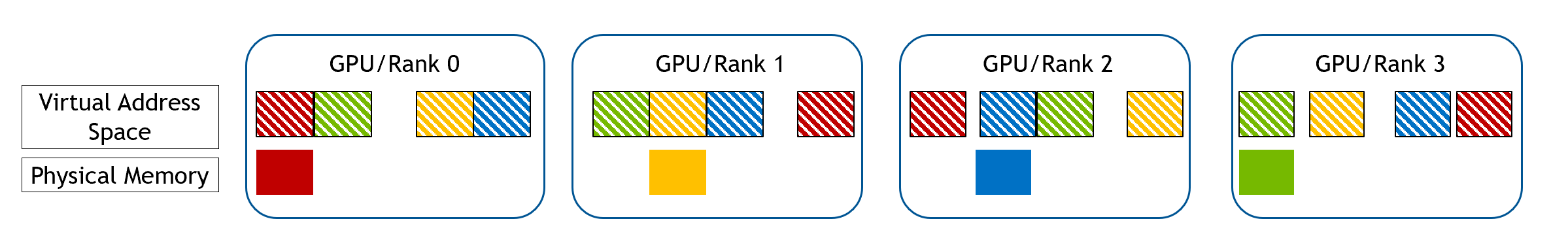
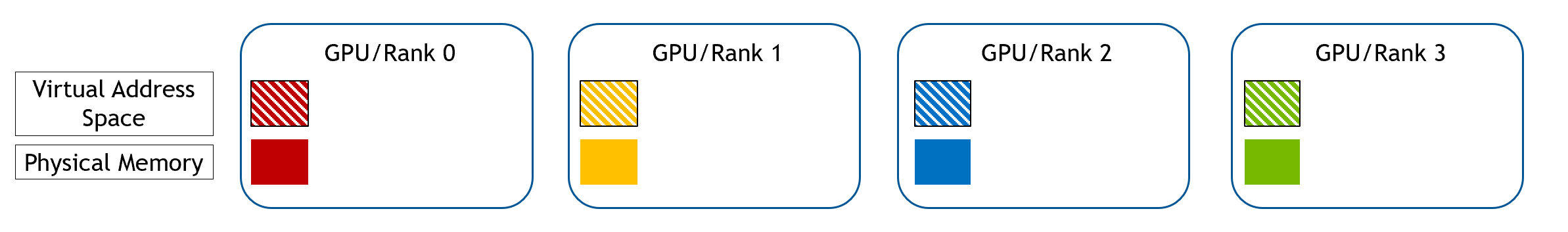 Each GPU gathers the Ipc handle of memory from all other GPUs, and maps that into its own virtual address space.
Each GPU gathers the Ipc handle of memory from all other GPUs, and maps that into its own virtual address space.
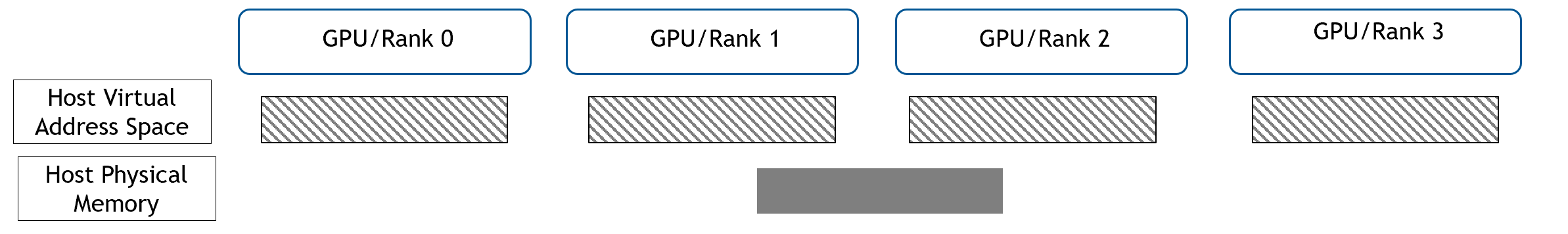
Host Mapped WholeMemory#
For Host, Continuous and Chunked are using the same method. First, rank and allocate the host physical and share that to all
ranks.
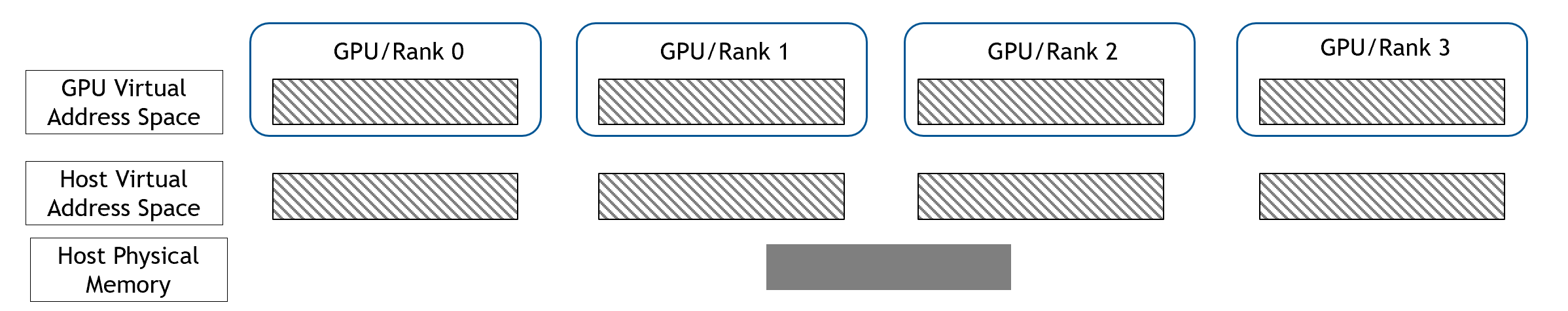
 Then each rank registers that host memory to GPU address space.
Then each rank registers that host memory to GPU address space.
Distributed WholeMemory#
For Distributed WholeMemory, each GPU just malloc its own part of memory, no need to share to other GPUs.
