RAFT ANN Benchmarks#
This project provides a benchmark program for various ANN search implementations. It’s especially suitable for comparing GPU implementations as well as comparing GPU against CPU.
Table of Contents#
Installing the benchmarks#
There are two main ways pre-compiled benchmarks are distributed:
Conda: For users not using containers but want an easy to install and use Python package. Pip wheels are planned to be added as an alternative for users that cannot use conda and prefer to not use containers.
Docker: Only needs docker and NVIDIA docker to use. Provides a single docker run command for basic dataset benchmarking, as well as all the functionality of the conda solution inside the containers.
Conda#
If containers are not an option or not preferred, the easiest way to install the ANN benchmarks is through conda. We provide packages for GPU enabled systems, as well for systems without a GPU. We suggest using mamba as it generally leads to a faster install time:
mamba create --name raft_ann_benchmarks
conda activate raft_ann_benchmarks
# to install GPU package:
mamba install -c rapidsai -c conda-forge -c nvidia raft-ann-bench=<rapids_version> cuda-version=11.8*
# to install CPU package for usage in CPU-only systems:
mamba install -c rapidsai -c conda-forge raft-ann-bench-cpu
The channel rapidsai can easily be substituted rapidsai-nightly if nightly benchmarks are desired. The CPU package currently allows to run the HNSW benchmarks.
Please see the build instructions to build the benchmarks from source.
Docker#
We provide images for GPU enabled systems, as well as systems without a GPU. The following images are available:
raft-ann-bench: Contains GPU and CPU benchmarks, can run all algorithms supported. Will download million-scale datasets as required. Best suited for users that prefer a smaller container size for GPU based systems. Requires the NVIDIA Container Toolkit to run GPU algorithms, can run CPU algorithms without it.raft-ann-bench-datasets: Contains the GPU and CPU benchmarks with million-scale datasets already included in the container. Best suited for users that want to run multiple million scale datasets already included in the image.raft-ann-bench-cpu: Contains only CPU benchmarks with minimal size. Best suited for users that want the smallest containers to reproduce benchmarks on systems without a GPU.
Nightly images are located in dockerhub, meanwhile release (stable) versions are located in NGC, starting with release 23.12.
The following command pulls the nightly container for python version 10, cuda version 12, and RAFT version 23.10:
docker pull rapidsai/raft-ann-bench:24.08a-cuda12.0-py3.10 #substitute raft-ann-bench for the exact desired container.
The CUDA and python versions can be changed for the supported values:
Supported CUDA versions: 11.2 and 12.0 Supported Python versions: 3.9 and 3.10.
You can see the exact versions as well in the dockerhub site:
Note: GPU containers use the CUDA toolkit from inside the container, the only requirement is a driver installed on the host machine that supports that version. So, for example, CUDA 11.8 containers can run in systems with a CUDA 12.x capable driver. Please also note that the Nvidia-Docker runtime from the Nvidia Container Toolkit is required to use GPUs inside docker containers.
How to run the benchmarks#
We provide a collection of lightweight Python scripts to run the benchmarks. There are 4 general steps to running the benchmarks and visualizing the results.
Prepare Dataset
Build Index and Search Index
Data Export
Plot Results
Step 1: Prepare Dataset#
The script raft_ann_bench.get_dataset will download and unpack the dataset in directory
that the user provides. As of now, only million-scale datasets are supported by this
script. For more information on datasets and formats.
The usage of this script is:
usage: get_dataset.py [-h] [--name NAME] [--dataset-path DATASET_PATH] [--normalize]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--dataset DATASET dataset to download (default: glove-100-angular)
--dataset-path DATASET_PATH
path to download dataset (default: ${RAPIDS_DATASET_ROOT_DIR})
--normalize normalize cosine distance to inner product (default: False)
When option normalize is provided to the script, any dataset that has cosine distances
will be normalized to inner product. So, for example, the dataset glove-100-angular
will be written at location datasets/glove-100-inner/.
Step 2: Build and Search Index#
The script raft_ann_bench.run will build and search indices for a given dataset and its
specified configuration.
The usage of the script raft_ann_bench.run is:
usage: __main__.py [-h] [--subset-size SUBSET_SIZE] [-k COUNT] [-bs BATCH_SIZE] [--dataset-configuration DATASET_CONFIGURATION] [--configuration CONFIGURATION] [--dataset DATASET]
[--dataset-path DATASET_PATH] [--build] [--search] [--algorithms ALGORITHMS] [--groups GROUPS] [--algo-groups ALGO_GROUPS] [-f] [-m SEARCH_MODE]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--subset-size SUBSET_SIZE
the number of subset rows of the dataset to build the index (default: None)
-k COUNT, --count COUNT
the number of nearest neighbors to search for (default: 10)
-bs BATCH_SIZE, --batch-size BATCH_SIZE
number of query vectors to use in each query trial (default: 10000)
--dataset-configuration DATASET_CONFIGURATION
path to YAML configuration file for datasets (default: None)
--configuration CONFIGURATION
path to YAML configuration file or directory for algorithms Any run groups found in the specified file/directory will automatically override groups of the same name
present in the default configurations, including `base` (default: None)
--dataset DATASET name of dataset (default: glove-100-inner)
--dataset-path DATASET_PATH
path to dataset folder, by default will look in RAPIDS_DATASET_ROOT_DIR if defined, otherwise a datasets subdirectory from the calling directory (default:
os.getcwd()/datasets/)
--build
--search
--algorithms ALGORITHMS
run only comma separated list of named algorithms. If parameters `groups` and `algo-groups are both undefined, then group `base` is run by default (default: None)
--groups GROUPS run only comma separated groups of parameters (default: base)
--algo-groups ALGO_GROUPS
add comma separated <algorithm>.<group> to run. Example usage: "--algo-groups=raft_cagra.large,hnswlib.large" (default: None)
-f, --force re-run algorithms even if their results already exist (default: False)
-m SEARCH_MODE, --search-mode SEARCH_MODE
run search in 'latency' (measure individual batches) or 'throughput' (pipeline batches and measure end-to-end) mode (default: throughput)
-t SEARCH_THREADS, --search-threads SEARCH_THREADS
specify the number threads to use for throughput benchmark. Single value or a pair of min and max separated by ':'. Example --search-threads=1:4. Power of 2 values between 'min' and 'max' will be used. If only 'min' is
specified, then a single test is run with 'min' threads. By default min=1, max=<num hyper threads>. (default: None)
-r, --dry-run dry-run mode will convert the yaml config for the specified algorithms and datasets to the json format that's consumed by the lower-level c++ binaries and then print the command to run execute the benchmarks but
will not actually execute the command. (default: False)
dataset: name of the dataset to be searched in datasets.yaml
dataset-configuration: optional filepath to custom dataset YAML config which has an entry for arg dataset
configuration: optional filepath to YAML configuration for an algorithm or to directory that contains YAML configurations for several algorithms. Here’s how to configure an algorithm.
algorithms: runs all algorithms that it can find in YAML configs found by configuration. By default, only base group will be run.
groups: run only specific groups of parameters configurations for an algorithm. Groups are defined in YAML configs (see configuration), and by default run base group
algo-groups: this parameter is helpful to append any specific algorithm+group combination to run the benchmark for in addition to all the arguments from algorithms and groups. It is of the format <algorithm>.<group>, or for example, raft_cagra.large
For every algorithm run by this script, it outputs an index build statistics JSON file in <dataset-path/<dataset>/result/build/<{algo},{group}.json>
and an index search statistics JSON file in <dataset-path/<dataset>/result/search/<{algo},{group},k{k},bs{batch_size}.json>. NOTE: The filenames will not have “,{group}” if group = "base".
dataset-path :
data is read from
<dataset-path>/<dataset>indices are built in
<dataset-path>/<dataset>/indexbuild/search results are stored in
<dataset-path>/<dataset>/result
build and search : if both parameters are not supplied to the script then
it is assumed both are True.
indices and algorithms : these parameters ensure that the algorithm specified for an index
is available in algos.yaml and not disabled, as well as having an associated executable.
Step 3: Data Export#
The script raft_ann_bench.data_export will convert the intermediate JSON outputs produced by raft_ann_bench.run to more
easily readable CSV files, which are needed to build charts made by raft_ann_bench.plot.
usage: data_export.py [-h] [--dataset DATASET] [--dataset-path DATASET_PATH]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--dataset DATASET dataset to download (default: glove-100-inner)
--dataset-path DATASET_PATH
path to dataset folder (default: ${RAPIDS_DATASET_ROOT_DIR})
Build statistics CSV file is stored in <dataset-path/<dataset>/result/build/<{algo},{group}.csv>
and index search statistics CSV file in <dataset-path/<dataset>/result/search/<{algo},{group},k{k},bs{batch_size},{suffix}.csv>, where suffix has three values:
raw: All search results are exportedthroughput: Pareto frontier of throughput results is exportedlatency: Pareto frontier of latency results is exported
Step 4: Plot Results#
The script raft_ann_bench.plot will plot results for all algorithms found in index search statistics
CSV files <dataset-path/<dataset>/result/search/*.csv.
The usage of this script is:
usage: [-h] [--dataset DATASET] [--dataset-path DATASET_PATH] [--output-filepath OUTPUT_FILEPATH] [--algorithms ALGORITHMS] [--groups GROUPS] [--algo-groups ALGO_GROUPS]
[-k COUNT] [-bs BATCH_SIZE] [--build] [--search] [--x-scale X_SCALE] [--y-scale {linear,log,symlog,logit}] [--x-start X_START] [--mode {throughput,latency}]
[--time-unit {s,ms,us}] [--raw]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--dataset DATASET dataset to plot (default: glove-100-inner)
--dataset-path DATASET_PATH
path to dataset folder (default: /home/coder/raft/datasets/)
--output-filepath OUTPUT_FILEPATH
directory for PNG to be saved (default: /home/coder/raft)
--algorithms ALGORITHMS
plot only comma separated list of named algorithms. If parameters `groups` and `algo-groups are both undefined, then group `base` is plot by default
(default: None)
--groups GROUPS plot only comma separated groups of parameters (default: base)
--algo-groups ALGO_GROUPS, --algo-groups ALGO_GROUPS
add comma separated <algorithm>.<group> to plot. Example usage: "--algo-groups=raft_cagra.large,hnswlib.large" (default: None)
-k COUNT, --count COUNT
the number of nearest neighbors to search for (default: 10)
-bs BATCH_SIZE, --batch-size BATCH_SIZE
number of query vectors to use in each query trial (default: 10000)
--build
--search
--x-scale X_SCALE Scale to use when drawing the X-axis. Typically linear, logit or a2 (default: linear)
--y-scale {linear,log,symlog,logit}
Scale to use when drawing the Y-axis (default: linear)
--x-start X_START Recall values to start the x-axis from (default: 0.8)
--mode {throughput,latency}
search mode whose Pareto frontier is used on the y-axis (default: throughput)
--time-unit {s,ms,us}
time unit to plot when mode is latency (default: ms)
--raw Show raw results (not just Pareto frontier) of mode arg (default: False)
mode: plots pareto frontier of throughput or latency results exported in the previous step
algorithms: plots all algorithms that it can find results for the specified dataset. By default, only base group will be plotted.
groups: plot only specific groups of parameters configurations for an algorithm. Groups are defined in YAML configs (see configuration), and by default run base group
algo-groups: this parameter is helpful to append any specific algorithm+group combination to plot results for in addition to all the arguments from algorithms and groups. It is of the format <algorithm>.<group>, or for example, raft_cagra.large
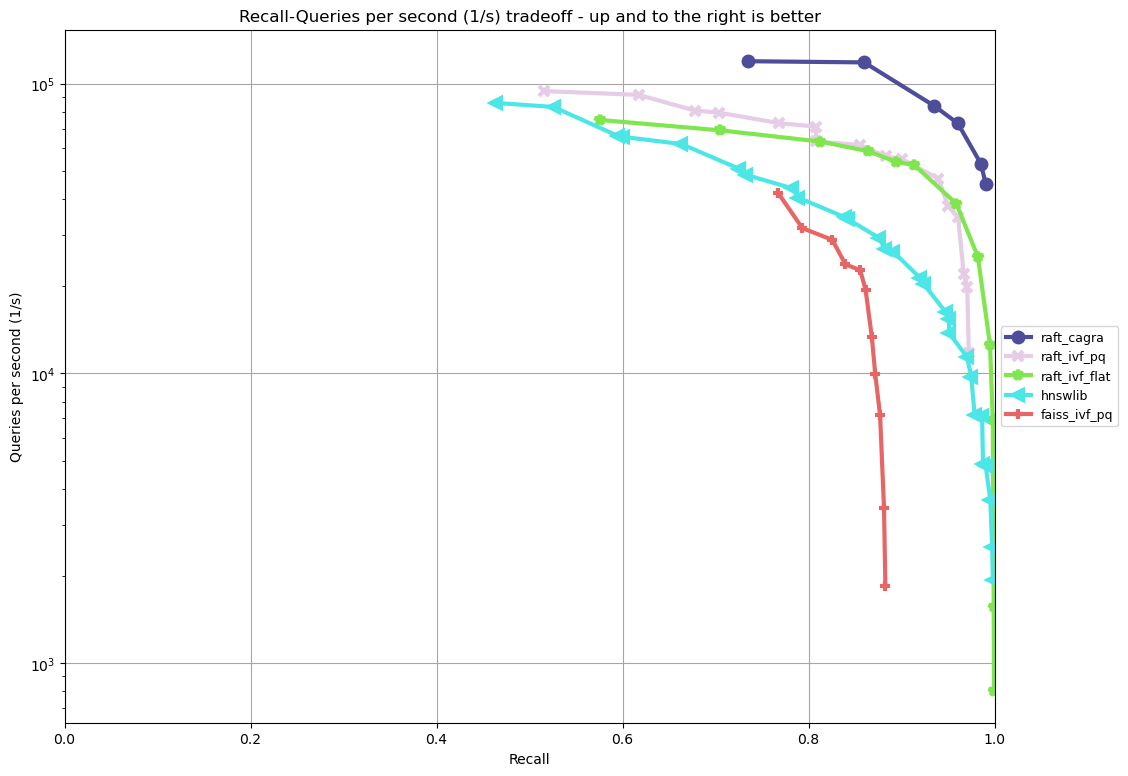
The figure below is the resulting plot of running our benchmarks as of August 2023 for a batch size of 10, on an NVIDIA H100 GPU and an Intel Xeon Platinum 8480CL CPU. It presents the throughput (in Queries-Per-Second) performance for every level of recall.
Running the benchmarks#
End to end: small-scale benchmarks (<1M to 10M)#
The steps below demonstrate how to download, install, and run benchmarks on a subset of 10M vectors from the Yandex Deep-1B dataset By default the datasets will be stored and used from the folder indicated by the RAPIDS_DATASET_ROOT_DIR environment variable if defined, otherwise a datasets sub-folder from where the script is being called:
# (1) prepare dataset.
python -m raft_ann_bench.get_dataset --dataset deep-image-96-angular --normalize
# (2) build and search index
python -m raft_ann_bench.run --dataset deep-image-96-inner --algorithms raft_cagra --batch-size 10 -k 10
# (3) export data
python -m raft_ann_bench.data_export --dataset deep-image-96-inner
# (4) plot results
python -m raft_ann_bench.plot --dataset deep-image-96-inner
Configuration files already exist for the following list of the million-scale datasets. Please refer to ann-benchmarks datasets for more information, including actual train and sizes. These all work out-of-the-box with the --dataset argument. Other million-scale datasets from ann-benchmarks.com will work, but will require a json configuration file to be created in $CONDA_PREFIX/lib/python3.xx/site-packages/raft_ann_bench/run/conf, or you can specify the --configuration option to use a specific file.
| Dataset Name | Train Rows | Columns | Test Rows | Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
deep-image-96-angular |
10M | 96 | 10K | Angular |
fashion-mnist-784-euclidean |
60K | 784 | 10K | Euclidean |
glove-50-angular |
1.1M | 50 | 10K | Angular |
glove-100-angular |
1.1M | 100 | 10K | Angular |
mnist-784-euclidean |
60K | 784 | 10K | Euclidean |
nytimes-256-angular |
290K | 256 | 10K | Angular |
sift-128-euclidean |
1M | 128 | 10K | Euclidean |
All of the datasets above contain ground test datasets with 100 neighbors. Thus k for these datasets must be less than or equal to 100.
End to end: large-scale benchmarks (>10M vectors)#
raft_ann_bench.get_dataset cannot be used to download the billion-scale datasets
due to their size. You should instead use our billion-scale datasets guide to download and prepare them.
All other python commands mentioned below work as intended once the
billion-scale dataset has been downloaded.
To download billion-scale datasets, visit big-ann-benchmarks
We also provide a new dataset called wiki-all containing 88 million 768-dimensional vectors. This dataset is meant for benchmarking a realistic retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)/LLM embedding size at scale. It also contains 1M and 10M vector subsets for smaller-scale experiments. See our Wiki-all Dataset Guide for more information and to download the dataset.
The steps below demonstrate how to download, install, and run benchmarks on a subset of 100M vectors from the Yandex Deep-1B dataset. Please note that datasets of this scale are recommended for GPUs with larger amounts of memory, such as the A100 or H100.
mkdir -p datasets/deep-1B
# (1) prepare dataset
# download manually "Ground Truth" file of "Yandex DEEP"
# suppose the file name is deep_new_groundtruth.public.10K.bin
python -m raft_ann_bench.split_groundtruth --groundtruth datasets/deep-1B/deep_new_groundtruth.public.10K.bin
# two files 'groundtruth.neighbors.ibin' and 'groundtruth.distances.fbin' should be produced
# (2) build and search index
python -m raft_ann_bench.run --dataset deep-1B --algorithms raft_cagra --batch-size 10 -k 10
# (3) export data
python -m raft_ann_bench.data_export --dataset deep-1B
# (4) plot results
python -m raft_ann_bench.plot --dataset deep-1B
The usage of python -m raft_ann_bench.split_groundtruth is:
usage: split_groundtruth.py [-h] --groundtruth GROUNDTRUTH
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--groundtruth GROUNDTRUTH
Path to billion-scale dataset groundtruth file (default: None)
Running with Docker containers#
Two methods are provided for running the benchmarks with the Docker containers.
End-to-end run on GPU#
When no other entrypoint is provided, an end-to-end script will run through all the steps in Running the benchmarks above.
For GPU-enabled systems, the DATA_FOLDER variable should be a local folder where you want datasets stored in $DATA_FOLDER/datasets and results in $DATA_FOLDER/result (we highly recommend $DATA_FOLDER to be a dedicated folder for the datasets and results of the containers):
export DATA_FOLDER=path/to/store/datasets/and/results
docker run --gpus all --rm -it -u $(id -u) \
-v $DATA_FOLDER:/data/benchmarks \
rapidsai/raft-ann-bench:24.08a-cuda11.8-py3.10 \
"--dataset deep-image-96-angular" \
"--normalize" \
"--algorithms raft_cagra,raft_ivf_pq --batch-size 10 -k 10" \
""
Usage of the above command is as follows:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
rapidsai/raft-ann-bench:24.08a-cuda11.8-py3.10 |
Image to use. Can be either raft-ann-bench or raft-ann-bench-datasets |
"--dataset deep-image-96-angular" |
Dataset name |
"--normalize" |
Whether to normalize the dataset |
"--algorithms raft_cagra,hnswlib --batch-size 10 -k 10" |
Arguments passed to the run script, such as the algorithms to benchmark, the batch size, and k |
"" |
Additional (optional) arguments that will be passed to the plot script. |
Note about user and file permissions: The flag -u $(id -u) allows the user inside the container to match the uid of the user outside the container, allowing the container to read and write to the mounted volume indicated by the $DATA_FOLDER variable.
End-to-end run on CPU#
The container arguments in the above section also be used for the CPU-only container, which can be used on systems that don’t have a GPU installed.
Note: the image changes to raft-ann-bench-cpu container and the --gpus all argument is no longer used:
export DATA_FOLDER=path/to/store/datasets/and/results
docker run --rm -it -u $(id -u) \
-v $DATA_FOLDER:/data/benchmarks \
rapidsai/raft-ann-bench-cpu:24.08a-py3.10 \
"--dataset deep-image-96-angular" \
"--normalize" \
"--algorithms hnswlib --batch-size 10 -k 10" \
""
Manually run the scripts inside the container#
All of the raft-ann-bench images contain the Conda packages, so they can be used directly by logging directly into the container itself:
export DATA_FOLDER=path/to/store/datasets/and/results
docker run --gpus all --rm -it -u $(id -u) \
--entrypoint /bin/bash \
--workdir /data/benchmarks \
-v $DATA_FOLDER:/data/benchmarks \
rapidsai/raft-ann-bench:24.08a-cuda11.8-py3.10
This will drop you into a command line in the container, with the raft-ann-bench python package ready to use, as described in the Running the benchmarks section above:
(base) root@00b068fbb862:/data/benchmarks# python -m raft_ann_bench.get_dataset --dataset deep-image-96-angular --normalize
Additionally, the containers can be run in detached mode without any issue.
Evaluating the results#
The benchmarks capture several different measurements. The table below describes each of the measurements for index build benchmarks:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Benchmark | A name that uniquely identifies the benchmark instance |
| Time | Wall-time spent training the index |
| CPU | CPU time spent training the index |
| Iterations | Number of iterations (this is usually 1) |
| GPU | GPU time spent building |
| index_size | Number of vectors used to train index |
The table below describes each of the measurements for the index search benchmarks. The most important measurements Latency, items_per_second, end_to_end.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Benchmark | A name that uniquely identifies the benchmark instance |
| Time | The wall-clock time of a single iteration (batch) divided by the number of threads. |
| CPU | The average CPU time (user + sys time). This does not include idle time (which can also happen while waiting for GPU sync). |
| Iterations | Total number of batches. This is going to be total_queries / n_queries. |
| GPU | GPU latency of a single batch (seconds). In throughput mode this is averaged over multiple threads. |
| Latency | Latency of a single batch (seconds), calculated from wall-clock time. In throughput mode this is averaged over multiple threads. |
| Recall | Proportion of correct neighbors to ground truth neighbors. Note this column is only present if groundtruth file is specified in dataset configuration. |
| items_per_second | Total throughput, a.k.a Queries per second (QPS). This is approximately total_queries / end_to_end. |
| k | Number of neighbors being queried in each iteration |
| end_to_end | Total time taken to run all batches for all iterations |
| n_queries | Total number of query vectors in each batch |
| total_queries | Total number of vectors queries across all iterations ( = iterations * n_queries) |
Note the following:
A slightly different method is used to measure
Timeandend_to_end. That is whyend_to_end=Time*Iterationsholds only approximately.The actual table displayed on the screen may differ slightly as the hyper-parameters will also be displayed for each different combination being benchmarked.
Recall calculation: the number of queries processed per test depends on the number of iterations. Because of this, recall can show slight fluctuations if less neighbors are processed then it is available for the benchmark.
Creating and customizing dataset configurations#
A single configuration will often define a set of algorithms, with associated index and search parameters, that can be generalize across datasets. We use YAML to define dataset specific and algorithm specific configurations.
A default datasets.yaml is provided by RAFT in ${RAFT_HOME}/python/raft-ann-bench/src/raft_ann_bench/run/conf with configurations available for several datasets. Here’s a simple example entry for the sift-128-euclidean dataset:
- name: sift-128-euclidean
base_file: sift-128-euclidean/base.fbin
query_file: sift-128-euclidean/query.fbin
groundtruth_neighbors_file: sift-128-euclidean/groundtruth.neighbors.ibin
dims: 128
distance: euclidean
Configuration files for ANN algorithms supported by raft-ann-bench are provided in ${RAFT_HOME}/python/raft-ann-bench/src/raft_ann_bench/run/conf. raft_cagra algorithm configuration looks like:
name: raft_cagra
groups:
base:
build:
graph_degree: [32, 64]
intermediate_graph_degree: [64, 96]
graph_build_algo: ["NN_DESCENT"]
search:
itopk: [32, 64, 128]
large:
build:
graph_degree: [32, 64]
search:
itopk: [32, 64, 128]
The default parameters for which the benchmarks are run can be overridden by creating a custom YAML file for algorithms with a base group.
There config above has 2 fields:
name- define the name of the algorithm for which the parameters are being specified.groups- define a run group which has a particular set of parameters. Each group helps create a cross-product of all hyper-parameter fields forbuildandsearch.
The table below contains all algorithms supported by RAFT. Each unique algorithm will have its own set of build and search settings. The ANN Algorithm Parameter Tuning Guide contains detailed instructions on choosing build and search parameters for each supported algorithm.
| Library | Algorithms |
|---|---|
| FAISS GPU | faiss_gpu_flat, faiss_gpu_ivf_flat, faiss_gpu_ivf_pq |
| FAISS CPU | faiss_cpu_flat, faiss_cpu_ivf_flat, faiss_cpu_ivf_pq |
| GGNN | ggnn |
| HNSWlib | hnswlib |
| RAFT | raft_brute_force, raft_cagra, raft_ivf_flat, raft_ivf_pq, raft_cagra_hnswlib |
Adding a new ANN algorithm#
Implementation and Configuration#
Implementation of a new algorithm should be a C++ class that inherits class ANN (defined in cpp/bench/ann/src/ann.h) and implements all the pure virtual functions.
In addition, it should define two structs for building and searching parameters. The searching parameter class should inherit struct ANN<T>::AnnSearchParam. Take class HnswLib as an example, its definition is:
template<typename T>
class HnswLib : public ANN<T> {
public:
struct BuildParam {
int M;
int ef_construction;
int num_threads;
};
using typename ANN<T>::AnnSearchParam;
struct SearchParam : public AnnSearchParam {
int ef;
int num_threads;
};
// ...
};
The benchmark program uses JSON format in a configuration file to specify indexes to build, along with the build and search parameters. To add the new algorithm to the benchmark, need be able to specify build_param, whose value is a JSON object, and search_params, whose value is an array of JSON objects, for this algorithm in configuration file. The build_param and search_param arguments will vary depending on the algorithm. Take the configuration for HnswLib as an example:
{
"name" : "hnswlib.M12.ef500.th32",
"algo" : "hnswlib",
"build_param": {"M":12, "efConstruction":500, "numThreads":32},
"file" : "/path/to/file",
"search_params" : [
{"ef":10, "numThreads":1},
{"ef":20, "numThreads":1},
{"ef":40, "numThreads":1},
],
"search_result_file" : "/path/to/file"
},
How to interpret these JSON objects is totally left to the implementation and should be specified in cpp/bench/ann/src/factory.cuh:
First, add two functions for parsing JSON object to
struct BuildParamandstruct SearchParam, respectively:template<typename T> void parse_build_param(const nlohmann::json& conf, typename cuann::HnswLib<T>::BuildParam& param) { param.ef_construction = conf.at("efConstruction"); param.M = conf.at("M"); if (conf.contains("numThreads")) { param.num_threads = conf.at("numThreads"); } } template<typename T> void parse_search_param(const nlohmann::json& conf, typename cuann::HnswLib<T>::SearchParam& param) { param.ef = conf.at("ef"); if (conf.contains("numThreads")) { param.num_threads = conf.at("numThreads"); } }
Next, add corresponding
ifcase to functionscreate_algo()(incpp/bench/ann/) andcreate_search_param()by calling parsing functions. The string literal inifcondition statement must be the same as the value ofalgo` in configuration file. For example,// JSON configuration file contains a line like: "algo" : "hnswlib" if (algo == "hnswlib") { // ... }
Adding a CMake Target#
In raft/cpp/bench/ann/CMakeLists.txt, we provide a CMake function to configure a new Benchmark target with the following signature:
ConfigureAnnBench(
NAME <algo_name>
PATH </path/to/algo/benchmark/source/file>
INCLUDES <additional_include_directories>
CXXFLAGS <additional_cxx_flags>
LINKS <additional_link_library_targets>
)
To add a target for HNSWLIB, we would call the function as:
ConfigureAnnBench(
NAME HNSWLIB PATH bench/ann/src/hnswlib/hnswlib_benchmark.cpp INCLUDES
${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/_deps/hnswlib-src/hnswlib CXXFLAGS "${HNSW_CXX_FLAGS}"
)
This will create an executable called HNSWLIB_ANN_BENCH, which can then be used to run HNSWLIB benchmarks.
Add a new entry to algos.yaml to map the name of the algorithm to its binary executable and specify whether the algorithm requires GPU support.
raft_ivf_pq:
executable: RAFT_IVF_PQ_ANN_BENCH
requires_gpu: true
executable : specifies the name of the binary that will build/search the index. It is assumed to be
available in raft/cpp/build/.
requires_gpu : denotes whether an algorithm requires GPU to run.